- Docker Tutorial
- Docker Useful Resources
We’ll introduce two different tools (dockerize and docker-compose-wait tool) to make docker compose wait for any service or dependencies to start. You can use these two solutions to deploy your application stack, particularly when you want: docker compose wait for mysql, docker compose wait for postgres, docker compose wait for redis. Docker Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. It allows users to launch, execute, communicate, and close containers with a single coordinated command. This guide will show you how to install Docker Compose on Ubuntu. Docker Compose allows you to define multi-container applications - or “stacks” - and run them either in their own Docker node or in a cluster.The tool provides command line commands for managing the entire lifecycle of your applications. In this guide, I’ll discuss a step by step installation of Docker and Docker Compose on Debian 10 (Buster). Docker is the most popular and widely used container runtime. It enables you to package and run your applications in isolated containers in a single server or cluster of Linux servers orchestrated by Kubernetes and similar tools.
Typically, when you execute docker-compose up, it will download and pull the appropriate image (if it is not cached locally on your server), it will then build the image using your application code, and finally start the whole docker application with all the dependencies.
- Selected Reading
Docker Compose is used to run multiple containers as a single service. For example, suppose you had an application which required NGNIX and MySQL, you could create one file which would start both the containers as a service without the need to start each one separately.
In this chapter, we will see how to get started with Docker Compose. Then, we will look at how to get a simple service with MySQL and NGNIX up and running using Docker Compose.
Docker Compose ─ Installation
The following steps need to be followed to get Docker Compose up and running.
Step 1 − Download the necessary files from github using the following command −
The above command will download the latest version of Docker Compose which at the time of writing this article is 1.10.0-rc2. It will then store it in the directory /home/demo/.
Step 2 − Next, we need to provide execute privileges to the downloaded Docker Compose file, using the following command −

We can then use the following command to see the compose version.
Syntax
Download Docker Compose Version 3
Parameters
version − This is used to specify that we want the details of the version of Docker Compose.
Output
The version details of Docker Compose will be displayed.
Example
The following example shows how to get the docker-compose version.
Output

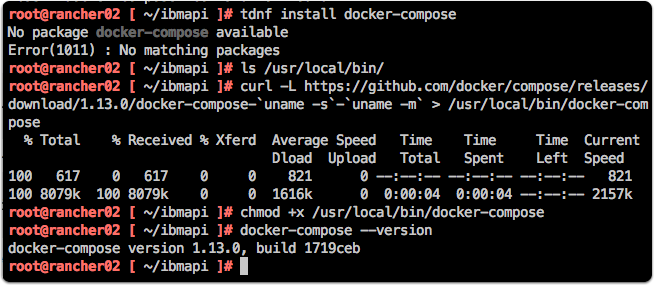
You will then get the following output −
Creating Your First Docker-Compose File
Now let’s go ahead and create our first Docker Compose file. All Docker Compose files are YAML files. You can create one using the vim editor. So execute the following command to create the compose file −
Let’s take a close look at the various details of this file −
Download Docker Compose
The database and web keyword are used to define two separate services. One will be running our mysql database and the other will be our nginx web server.
The image keyword is used to specify the image from dockerhub for our mysql and nginx containers
For the database, we are using the ports keyword to mention the ports that need to be exposed for mysql.
And then, we also specify the environment variables for mysql which are required to run mysql.

Now let’s run our Docker Compose file using the following command −
This command will take the docker-compose.yml file in your local directory and start building the containers.
Once executed, all the images will start downloading and the containers will start automatically.
And when you do a docker ps, you can see that the containers are indeed up and running.